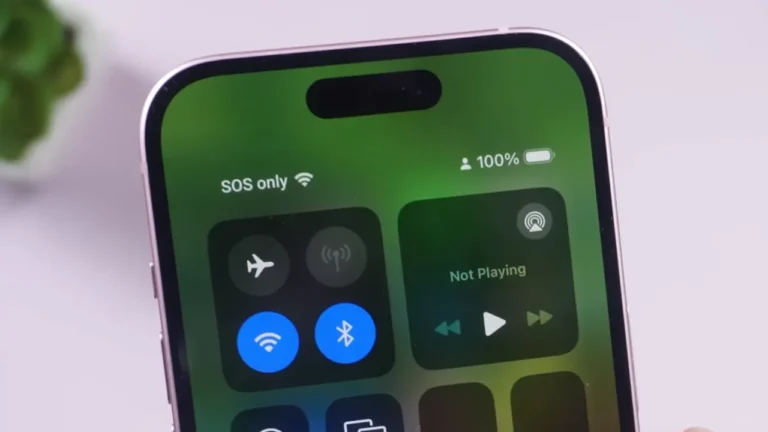
When your iPhone displays “SOS” or “SOS Only” in the status bar, it means your device can’t reach your carrier’s network, and it’s falling back to emergency-only access. Normal calls, texts, and mobile data are unavailable, but emergency SOS calling still works through any network Apple is allowed to use in your region. The feature is currently supported in the U.S., Canada, and Australia. Though most causes are simple, usually linked to network conditions, SIM issues, or device settings, and many of these fixes won’t take more than a few minutes to solve the ‘SOS Only’ status on iPhone.
What Does SOS Only Mean on an iPhone?
The iPhone’s “SOS Only” is a special feature Apple introduced to allow iPhone users to make emergency calls via a satellite network, even when their device is out of their carrier provider’s cellular network. It appears when the phone detects any network in the area other than yours. Apple allows the device to connect with emergency infrastructure even without a carrier’s internet in that region, which is mostly the case when you travel abroad.

It’s not the same as No Service, where your device won’t connect to anything, not even for emergencies. SOS Only also has nothing to do with the Emergency SOS feature, which is the manual action that calls emergency services when you press and hold the side button and a volume button for 2 seconds. Here, the phone isn’t stuck in that mode; it is just unable to authenticate with your mobile provider.
When the device is in ‘SOS Only’ mode, only these functions will work:
- Emergency calls
- Location sharing with emergency services
- Normal calls, SMS, and mobile data don’t
- Wi-Fi-based apps (FaceTime, WhatsApp, Messenger, etc.) only on Wi-Fi
If you reconnect to your cellular data, this emergency mode will be disabled immediately.
Why Does iPhone Show SOS Only?
There are a lot of conditions that can lead your Apple device into Emergency SOS, such as:
- Your carrier’s signal isn’t available: Remote areas, underground parking, buildings with heavy insulation, rural travel, or simple dead zones can push your phone into SOS Only. The same is the case with carrier outages due to weather or network maintenance.
- SIM or eSIM isn’t registering correctly: A worn SIM, a misaligned tray, an inactive plan, or a damaged profile (for eSIM users) can prevent authentication. Old SIM cards often don’t work after major iOS or carrier updates.
- Incorrect network or roaming settings: ‘SOS Only’ mode can also happen if you travel internationally but don’t enable the roaming option, change your network, or use an incompatible network configuration
- Software bugs or outdated carrier settings: iOS bugs can also cause intermittent signal issues. Carrier settings updates (different from iOS updates) are more important than most people expect because they control the rules your phone uses to connect to the network.
- Hardware problems: A drop, impact, or liquid damage can affect antenna modules. When that happens, the phone struggles to lock onto your carrier’s frequencies when other networks are present around.
How to Tell If Your iPhone is in SOS Only Mode
Look at the top-right corner of the iPhone screen to see the status that appears in place of your SIM name. But before you try fixes, first confirm it’s the real reason. It happens when:
- The carrier name disappears, and you only see SOS or SOS Only.
- Cellular Data shows inactive or disconnected in Settings > Cellular.
- Airplane Mode is disabled, but you can’t connect to the network.
- The device goes to SOS instantly after a restart.
Once you confirm that the device struggles to reconnect automatically, it’s time to re-establish the network link.
How to Fix SOS Only on iPhone
Reset the Network Connection
First, turn on Airplane Mode to force the phone to relink with nearby towers. In Airplane Mode, the device stops all radios. After 15 seconds, disable the mode and reconnect the iPhone to the network, which allows the device to start fresh and search for available networks.
If it’s a temporary authentication failure or local congestion, this simple step can fix it. But if it doesn’t work, restart your iPhone to reset all low-level network services, which include modem firmware.
Confirm Cellular Data Settings
Sometimes ‘SOS Only’ shows because mobile data was turned off or the phone is set to use the wrong network mode. Open Settings > Cellular and confirm that Cellular Data is enabled.
On iPhones with 5G and LTE options, switch between these network types—occasionally, a specific band in your area may be unstable. For Network Selection, turn off Automatic and choose the carrier manually to see if the device detects the network.
Check Your SIM or eSIM
A physical SIM with scratches, dust, or age-related wear can fail unexpectedly. So remove, clean, and reinsert it. If the SIM was transferred from an old phone, it might not be properly provisioned for the latest network technology. If yo use eSIM, open Settings > Cellular and verify the plan is active. A corrupted eSIM profile can be removed and re-added from your carrier’s app or by contacting support.
Update iOS and Carrier Settings
- iOS: A major iOS update usually includes modem and network stability improvements. To update iOS to the latest version, go to Settings > General and select Software Update.
- Carrier Settings: It’s the configuration bundle carrier provider offers to enable VoLTE, 5G bands, roaming rules, and SMS/MMS routing. To make sure it’s up to date, open Settings > General and then tap About. If an update is available, the phone will show a prompt under this section.
Check Roaming Settings if You’re Abroad
If you’re out of the country, ‘SOS’ is mostly only a missing roaming toggle. In Settings > Cellular, tap Cellular Data Options, and enable Data Roaming. Be aware of roaming charges. If you prefer not to pay, a prepaid SIM or travel eSIM is the better option.
Reset Network Settings (When Simple Fixes Don’t Work)
Network reset will wipe Wi-Fi passwords and all custom network settings, so first back them up in a safe place to access later. If corrupted network data is the reason, the most reliable method is to reset it. Head to Settings > General > Transfer or Reset iPhone and select Reset Network Settings.
Reinstall iOS via Recovery Mode
If the iPhone’s network stack is corrupted at the system level, a simple restart won’t get the job done. Recovery Mode forces the device to reload iOS and its modem firmware from a clean image via Finder or iTunes. It’s not a preferred step, but when every other fix fails, and the phone remains locked in ‘SOS Only’, a full reinstall is sometimes the only way to clear the underlying fault.
Hardware Issue
Physical damage is a common reason an iPhone can see nearby networks yet fail to authenticate with its own carrier. A drop, flex, or liquid exposure can damage the cellular antennas or their internal connections. In that state, the phone may detect emergency-only signals but lack the stability for regular service, which is why ‘SOS’ status is activated instead of No Service. Apple Diagnostics or a qualified technician can confirm whether the issue is hardware-related.
Contact Your Carrier
When the device itself checks out, the problem will likely be on the carrier side. Support teams can test if your line is active, the IMEI is flagged or unregistered, whether there’s an outage in your area, or if the SIM/eSIM profile failed to provision correctly. They can also refresh the carrier configuration on your number—something users can’t do manually, and a fix that resolves many pesky cases.
How to Reduce the Chances of Seeing SOS Only on iPhone
You can’t prevent all network dropouts, but you can make them less frequent.
- Keep iOS and carrier settings updated.
- Use a modern SIM or eSIM profile.
- Turn on roaming before traveling to prevent lockouts abroad.
- Avoid signal-challenged areas when possible.
- Be aware of where your carrier has known dead zones.
These steps won’t stop emergencies or outages, but they’re a better way to keep everyday connectivity more stable.