HDR has become one of the key features you’ll see on all sorts of modern gadgets like your TV, computer monitor, smartphone camera, and even the latest gaming consoles, and it’s no longer just a buzzword splashed on a box. HDR makes a big difference to how our displays work, letting them show a wider spread of brightness, shadow detail, and color that seemed impossible a few years back. When it’s done well, it’s one of the clearest and most noticeable upgrades in visual tech right now. Though a few segments make it hard for ordinary people to understand High Dynamic Range. This guide explains what HDR means, how it works, its formats, and where it is used.
Dynamic Range on Displays
Dynamic range is the range of brightness that a display can manage from the darkest blacks to the brightest whites. The old SDR (Standard Dynamic Range) video was cobbled together from the limitations of some very outdated broadcast standards, where blacks were only to be so dark, and whites could only be so bright.
Nowadays, the newer display hardware like OLED panels and even some quality LED/LCD sets with good local dimming can push these limits much further. Some screens can hit an incredible 1,000, 2,000, or even more nits on highlights, and OLED pixels can drop so low in black that they measure zero. But it doesn’t matter how bright or dark your screen can go if the video signal itself doesn’t have the information to fill in those missing levels, and that’s where HDR comes in.
What is HDR (or High Dynamic Range)?
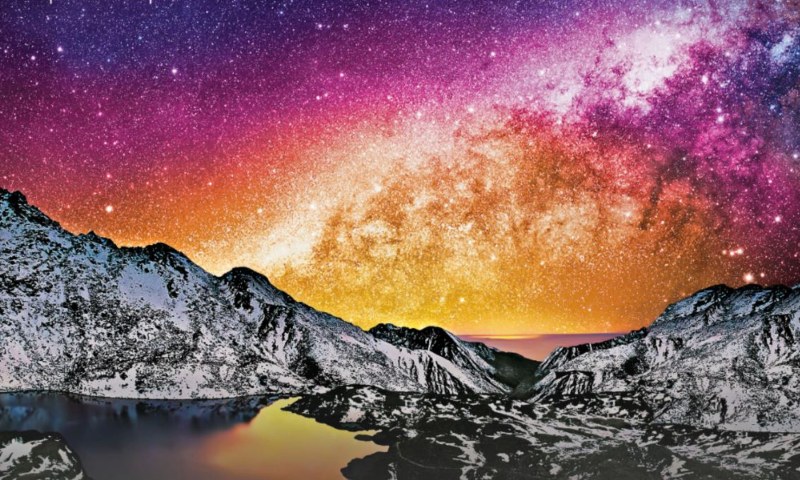

HDR video breaks past the brightness and color limits of old standards. Traditional signals compress everything into a narrow window, which forces displays to invent missing steps by processing. HDR manages that by encoding a far broader range of luminance and color directly into the signal. An HDR display can read these values and render real gradations, and that includes from deep shadows through midtones to intense highlights.
Practically, HDR allows a screen to show real bright elements and genuine dark, and preserve the fine detail. The image contains more increments between black and white, so you see better transitions than clipped or crushed. There’s also more nuance in saturated colors: reds, greens, and blues can have deep intensities with small variations than flattening into a single shade. Though how it can work depends heavily on the display’s hardware. A strong HDR TV has enough peak brightness, low black levels, and color volume to take advantage of the extra information. A weak set might accept the HDR signal but struggle to reproduce its full range, which is pointless.
Because HDR carries much more data, not every media format can handle it. You rarely see standard Blu-ray discs making the cut because they don’t have the capacity and bandwidth to deal with it. Ultra HD Blu-ray discs, on the other hand, are specifically designed to handle the high-quality 4K resolution, HDR video, and advanced audio formats like Dolby Atmos, but require compatible players or the latest consoles. Not all screens can take full advantage of HDR metadata. Some have the right decoder but no luminance or color volume to give the full effect. That’s why HDR varies largely between displays.
HDR and Color Gamut
Dynamic range deals strictly with luminance, but brightness and color perception are linked, so a wide light range enables a wide range of perceivable color. That’s why many HDR screens also support a wide color gamut (WCG), and it often covers almost all cinema-grade DCI-P3 color space. WCG expands way beyond Rec.709, the color space used in standard TV. Still, HDR doesn’t have any guarantee of wide gamut coverage. They are two separate elements, even if they work side by side on premium displays. Usually, testing is needed to figure out how much of P3 or Rec.2020 a given display can reproduce.
Types of HDR
HDR has a couple of main formats and a few less common ones because different parts of the industry like studios, streaming platforms, TV manufacturers, and broadcasters, solved the same problem in different ways. The main difference between these formats is how they communicate brightness and color information to a display. Some formats take a “set it once” approach, while others actively guide the TV frame by frame.
HDR10
HDR10 is the foundation of modern HDR delivery. It’s an open, royalty-free standard, which is why virtually every HDR-capable TV, monitor, console, and streaming app supports it by default. In HDR10, the peak brightness, black level, and color volume are fed into the video as static metadata. Static metadata means the display receives one set of instructions for the complete piece of content. The TV then performs its own tone-mapping to fit the values into whatever range its panel can physically produce.
Because HDR10 is built around 10-bit color, it can describe far more luminance steps and color variations than SDR. Due to simplicity and lack of licensing fees, it is the universal HDR baseline, but static metadata can leave some scenes underoptimised on limited dynamic range displays.
HDR10+
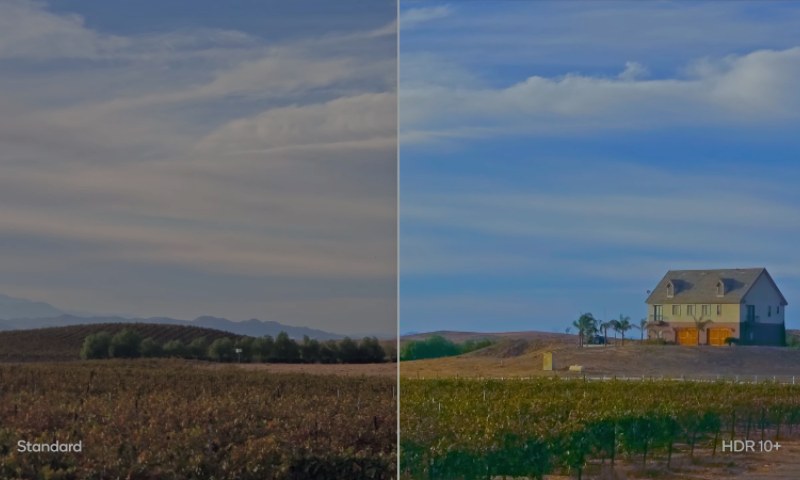

HDR10+ was Samsung’s answer to the restrictions of static metadata. It keeps HDR10’s open, license-free nature but replaces its single global instruction set with dynamic metadata, so brightness and tone adjustments can vary scene by scene or shot by shot. It gives the mastering studio better control and lets the display map every content segment with more accuracy to its abilities.
In practice, HDR10+ can keep more highlight detail in bright sequences and retain clean shadow structure in darker levels than HDR10. Its industry support is less than Dolby Vision, but some big streaming platforms, including YouTube, Prime Video, and Hulu, use HDR10+ for streams.
Dolby Vision
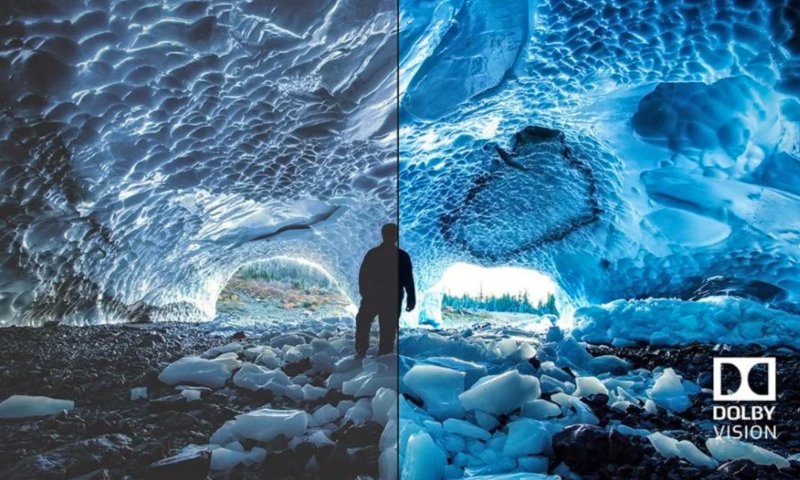

Dolby Vision is the most fully featured HDR format, and the only major one that needs a license for media and screens to be Dolby Vision supported. It also uses dynamic metadata, but its workflow goes further: the mastering process is done with the assumption that end-user displays vary widely in brightness, color volume, and tone-mapping behaviour. Dolby Vision content contains instructions that allow a TV to adapt the signal to its own performance envelope.
Because of this per-display optimization, Dolby Vision usually preserves highlight detail and deep shadow content more reliably than static HDR formats on mid-range hardware. It’s also the most widely supported dynamic metadata format across premium streaming services and high-end TVs. Though Dolby Vision needs certification and specific production workflows, and some device makers run away from this headache.
HLG (Hybrid Log-Gamma)

HLG completely takes a different approach. Developed by the BBC and NHK for broadcasters, it was built to work in real-time environments where metadata is impractical. Instead of using static or dynamic metadata, HLG operates on a hybrid transfer curve that mixes an SDR gamma response with a logarithmic section for highlights. An HLG signal can thus be displayed by SDR sets without extra processing and by HDR sets with a broader highlight range.
Due to this principle, HLG is better for live TV, sports, and news—any environment where compatibility and low latency matter more than extreme brightness and dark accuracy. But we won’t see it much adopted outside broadcast. Still, HLG is a technically important part of the HDR section because it solves a different problem than HDR10 or Dolby Vision.
HDR and Color Depth
HDR video relies on increased color precision. Traditional 8-bit video offers 256 brightness steps per channel. HDR typically uses 10-bit (1,024 steps) or 12-bit (4,096 steps), which reduces banding and enables good gradients—important when content spans a wide luminance range and a large color space. Games and rendering engines mostly work internally at 16- or 32-bit floating point, then tone map down to HDR10 or Dolby Vision to display output.
How Displays Render HDR
HDR performance depends greatly on the kind of panel that powers the screen. Both OLED and LCD technologies are HDR compatible, but they go about it in different ways.
OLED panels create light at the pixel level. Every pixel is its own light source, so when a scene calls for deep blacks, the pixel shuts off. It gives OLED a clear advantage in contrast, when black levels drop to near zero, and bright elements stand out without haloing. Although OLED can’t reach the brightness levels as of high-end Mini-LED screens, the combination of perfect blacks and precision control at the pixel level gives some of the most convincing HDR images you’re ever likely to see. Specular highlights on OLED might be low in absolute nit, but due to the high contrast ratio, the impact remains pretty good.
LCD with LED or Mini-LED backlighting works in a different way. The displays rely on a backlight shining through liquid crystals, so the panel can’t naturally achieve OLED-like black levels. Manufacturers overtake it by increasing peak brightness and controlling the backlight in zones. High-end Mini-LED panels use thousands of tiny LEDs grouped into hundreds or even thousands of local dimming zones. When there are enough zones, the display can darken specific regions and drive others to high brightness, like 1,000 to 4,000 nits on top-end models. This is why Mini-LED is strong in well-lit environments, where OLEDs struggle with the lower peak brightness.
When it comes to real-world HDR performance, it all comes down to how well the display handles things like blooming, shadow detail, colour volume, and, of course, brightness. OLEDs lead in darkened rooms to present a cinematic view, while Mini-LED generally does better in well-lit rooms thanks to its extreme brightness headroom. They far outperform basic edge-lit LCDs, which just accept an HDR signal and can’t deliver reliable HDR contrast.
To differentiate great HDR hardware from nominal support, manufacturers take part in certification programs like DisplayHDR. The low tiers (such as 400) indicate little more than signal compatibility, and the mid and upper tiers—600, 1000, 1400, and the “True Black” categories—set expectations for sustained brightness, black-level performance, and color accuracy. Although these certifications aren’t 100% reliable, they’re still a useful way to weed out anything that doesn’t even meet the basics of HDR.
HDR Content and Playback Requirements
HDR only works when every part of the chain, including display, device, and content, supports it. The display must understand HDR metadata, the playback hardware should pass it through, and the content must be in an HDR format. Physical media like Ultra HD Blu-ray is one of the most reliable HDR sources. Every UHD disc supports HDR10, and many titles also come with Dolby Vision. These discs store higher bitrates than streaming platforms, so they are a benchmark for consistent HDR results.
Streaming services have the most common HDR delivery method right now. Platforms including Netflix, Disney+, Apple TV+, Prime Video, YouTube, and Hulu deliver HDR titles in HDR10, Dolby Vision, or HDR10+. Every service has its own catalog and preferred media format. To stream content on a smart TV app or an external device, the player must support the same HDR profile as the service and your display panel.
Game consoles are special, as they play HDR video and also output HDR games. PS5 and Xbox Series X support HDR10, with Dolby Vision for streaming apps and select Xbox titles. But even so, HDR gaming can be a little headache because the in-game brightness needs a tweak to the display’s brightness range.
The thing that can hold you back with streaming is your internet speed. You need a good connection to get HDR to work, especially in 4K. Many streaming services recommend an internet speed of at least 15-25 Mbps so you don’t get compression artifacts or dropped quality in video. When the display, device, and content all speak the same language, HDR really shines, delivering the full range of brightness, color, and shadow detail that it was meant for.