Do you know that almost everything you do on your Android device, from checking your favorite websites to scrolling through social media, starts with a Domain Name System (DNS) query? DNS is like the internet’s phonebook which helps your device find the correct IP address for the websites you want to visit. But these queries are often not encrypted, which means anyone on the same network can see what you’re up to. That’s where Private DNS Mode on Android plays its part. It not only secures your online activities but also gives you peace of mind when connecting to public Wi-Fi. This article breaks down how you can turn Private DNS Mode on and why it’s important for privacy.
Why You Should Use Private DNS Mode?
Whenever you’re online, DNS requests are sent as plain text. Think of it like sending postcards—everyone who handles it can see what’s written. This lack of encryption is particularly a great privacy threat on public networks, like when you’re using Wi-Fi at a coffee shop or the airport. If a bad actor is on the same network, they could easily intercept your DNS queries, revealing which websites you’re visiting or even hijacking your connection.
That’s why Private DNS Mode is so important. By encrypting your DNS queries using DNS over TLS, it ensures that all your data remains private. No one can snoop on your internet traffic, and it protects you from cyber threats such as DNS spoofing or man-in-the-middle attacks.
In short, using Private DNS on your Android device helps you stay secure, particularly in vulnerable environments like public Wi-Fi.
How to Enable Private DNS Mode on Android
Ready to lock down your DNS queries? Here’s a simple step-by-step guide to turning on Private DNS Mode on your Android device:
Start by going to the Settings on your phone. You can do this from the notification bar or directly from your app drawer.
Once in Settings, scroll until you find Network & Internet. Tap on it. For Samsung Galaxy users, the process is slightly different; you need to move to More Connection Settings.
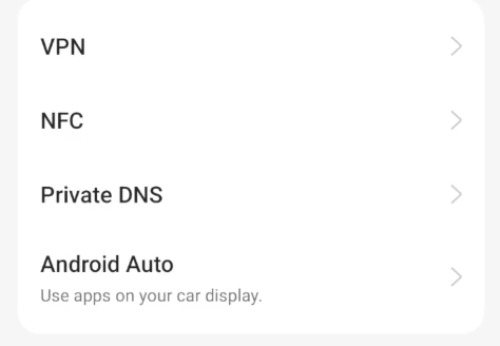
Find and go to Private DNS. If you can’t find it right away, use the search bar in the Settings app and type “Private DNS” to jump directly to the option.

In the menu, you’ll see three options:
- Off: This disables Private DNS.
- Automatic: Your phone will attempt to use encrypted DNS when available, but you’re reliant on your ISP or mobile network supporting it.
- Private DNS Provider Hostname: This is where you can manually enter the hostname of a secure DNS provider.
We recommend using Cloudflare (1dot1dot1dot1.cloudflare-dns.com) or Google DNS (dns.google) as they offer fast, reliable, and secure DNS services. Once you’ve entered the hostname, tap Save to lock in your settings.
Which DNS Provider Should You Choose?
You can use several DNS providers to ensure your queries stay encrypted. Here are a few popular choices:
- Cloudflare:
1dot1dot1dot1.cloudflare-dns.com(Our top pick for speed and security) - Google DNS:
dns.google - Quad9:
dns.quad9.net - OpenDNS:
208.67.222.222 - CleanBrowsing:
security-filter-dns.cleanbrowsing.org
Each provider is designed to enhance your privacy while speeding up your browsing. We recommend experimenting with different ones to see which works best for your location and network speed.
Benefits of Using Private DNS Mode
There are plenty of perks to using the private DNS mode on the handset. These are the factors why it is well worth the few minutes it takes to set up:
- Improved Privacy: Your DNS queries are encrypted, so third parties like your Internet Service Provider (ISP) or hackers can’t easily track your browsing data.
- Security on Public Networks: There is a higher risk of cyberattacks when connected to the public Internet. Private DNS safeguards your data by encrypting traffic between your device and the DNS provider.
- Bypass Geographical Restrictions: Some DNS services, like Cloudflare or Google DNS, can even help you access the restricted content based on your location. While it’s not a guaranteed solution, it can work in some cases.
- Improved Speed and Reliability: Many third-party DNS services offer faster resolution times than your ISP’s default server, you may find some improvement in your Internet after enabling this DNS. A few of these providers put a lock on malicious sites, adding an extra security layer of security.
How to Check If My ISP Supports Private DNS?
There are some ways you can check if your Internet company supports Private DNS. One of them is to use a web tool like Tenta’s Browser Privacy Test, which shows if your ISP’s DNS is TLS enabled or not. Another option is to verify the authority of the reply by doing a DNS lookup to a nameserver using a command-line tool such as dig or nslookup. When your Internet service provider (ISP) does not reroute or intercept your DNS queries, you will receive authoritative replies.
You can also try to use custom DNS by going into Settings > Network & Internet or More Connection Settings > Private DNS > Private DNS provider hostname enter any public DNS hostname and click on Save. If you see a message saying “Couldn’t connect”, it means your ISP does not support Private DNS or the DNS server you entered is not valid.