Ray tracing is still the crucial object in graphics, and Nvidia doesn’t want to slow down to find new ways to achieve more frames through tracing. The latest development comes from a research paper spotted by 0x22h, where Nvidia and academic collaborators detail GPU Subwarp Interleaving. On paper, it sounds simple enough; reorganize how the GPU schedules threads, and ray tracing performance can increase by up to 20%.
Of course, nothing’s ever that simple in graphics card space. This isn’t a driver trick or some easy firmware patch. To make Subwarp Interleaving work, Nvidia would need to bake it into the microarchitecture itself. Your current RTX 30-series won’t get fast ray tracing, no matter how many “Game Ready” drivers you install, this is future-silicon stuff.
Why Ray Tracing Trips Up GPUs
To understand why Nvidia is after this, you should see how GPUs are built today. In the SIMT (single instruction, multiple threads) model, Nvidia GPUs use a single program counter to issue instructions to a bundle of threads called a “warp.” When one warp stalls on memory or branching, the scheduler hides the delay by swapping in another warp.
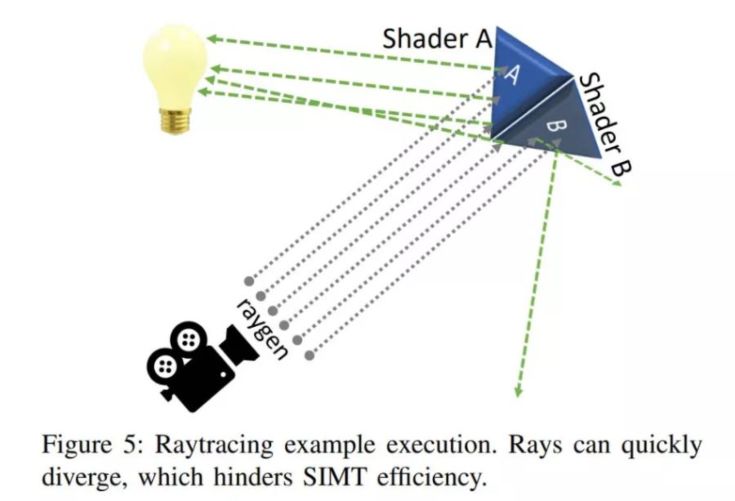
Ray tracing, though, is a scheduling nightmare. Rays bounce around unpredictably, workloads spread in different directions, and your warps aren’t nicely aligned anymore. The result is “warp divergence” and “warp starvation,” which is a modern way of saying the scheduler starts running out of useful work to do. Once you can’t hide latency with another warp, performance tanks.
The proposed solution? Instead of waiting for an entire warp to be ready, split it into smaller “subwarps” and let the scheduler interleave them.
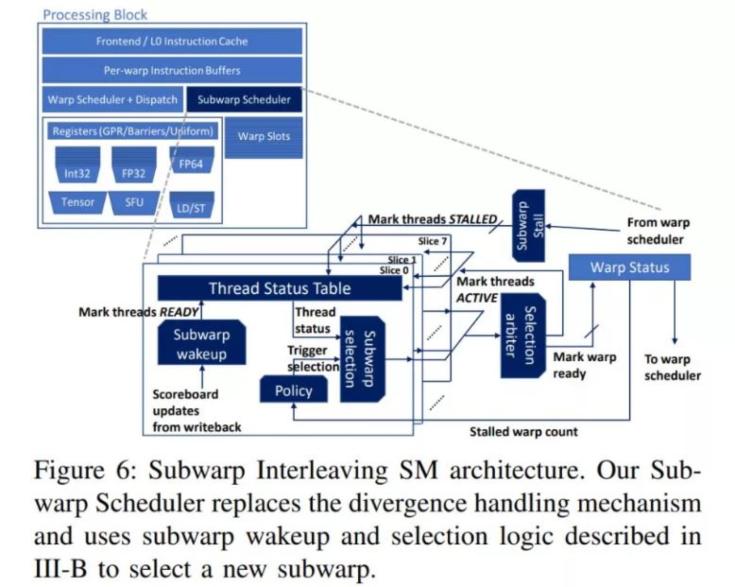
The researchers, including GIT professor Sana Damani and Nvidia engineers like Ram Rangan and Stephen W. Keckler, tested the idea on a modified Turing-like GPU. The results weren’t just academic rounding errors, across a suite of ray tracing workloads, performance improved by an average of 6.3%, with the best-case hitting nearly 20%. For real-time graphics, that’s the difference between “playable” and “actually smooth.”
But this isn’t a feature you’ll see automatically unlocked on your RTX 3080 via a driver update. Subwarp Interleaving requires changes in the architecture. Nvidia would need to redesign future GPUs with this scheduler built in from the start. That means the earliest you’ll see it is in a next-gen family like Lovelace, Hopper, or whatever codename Team Green wants to attach.
That’s how GPU R&D usually works. You see a research paper here, a SIGGRAPH demo there, and then two or three years later, it appears in shipping silicon under some marketing-friendly label like “RTX Ray Accelerator 2.0.”
Nvidia is still investing a lot in ray tracing performance. Real-time ray tracing is expensive, even on today’s fastest GPUs. Every generation, Nvidia has rolled out something to keep its lead first RT cores, then DLSS to soften the blow, and now experimental scheduler tweaks like Subwarp Interleaving.
Even if this particular idea doesn’t ship exactly as-is, it’s part of a long-term strategy that’s to keep iterating on the architectural bottlenecks that make ray tracing so resource-hungry. AMD has been catching up with its RDNA2 implementation, but Nvidia wants to stay a step ahead, and these microarchitecture-level optimizations are how they plan to do it.







